How we tackle it
A EXPLORATION ENVIRONMENT. We propose a smart literature analysis environment, which includes several NLP-powered components to enable a more efficient reading process. The following two strategies are the core of our environment.
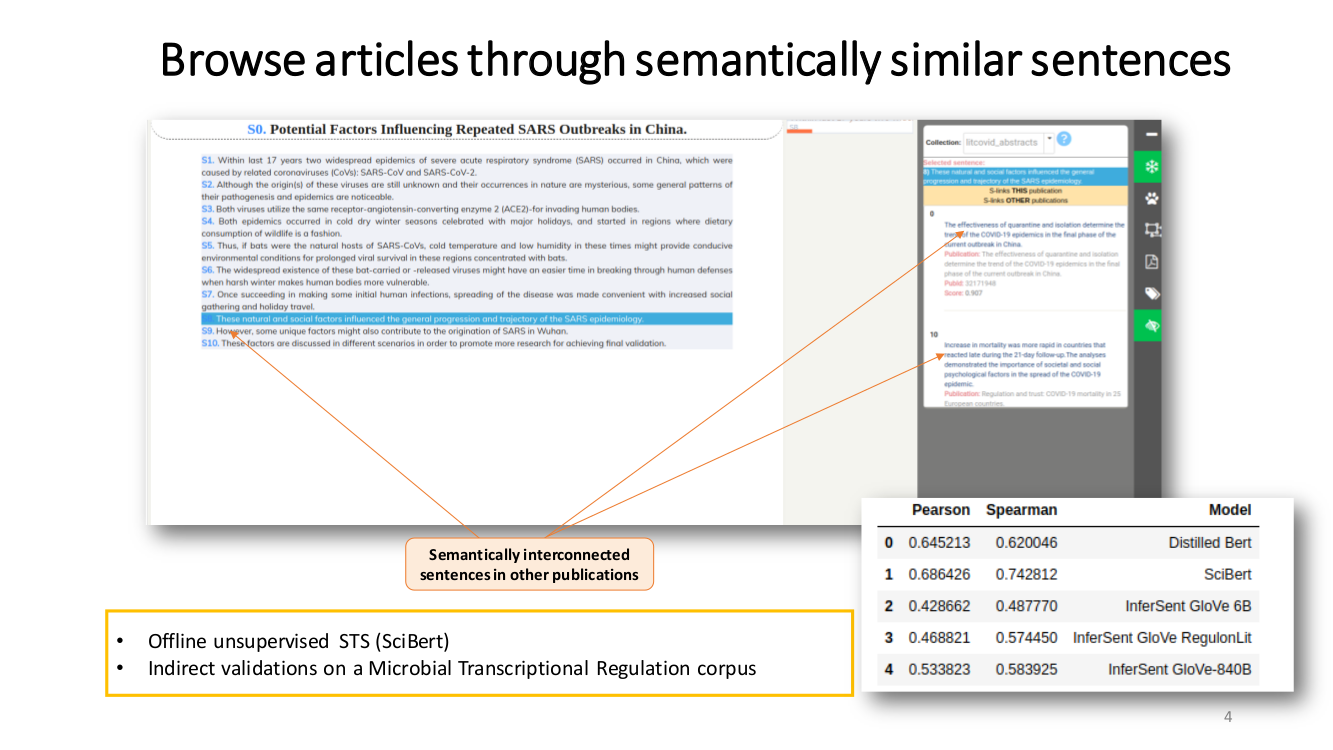
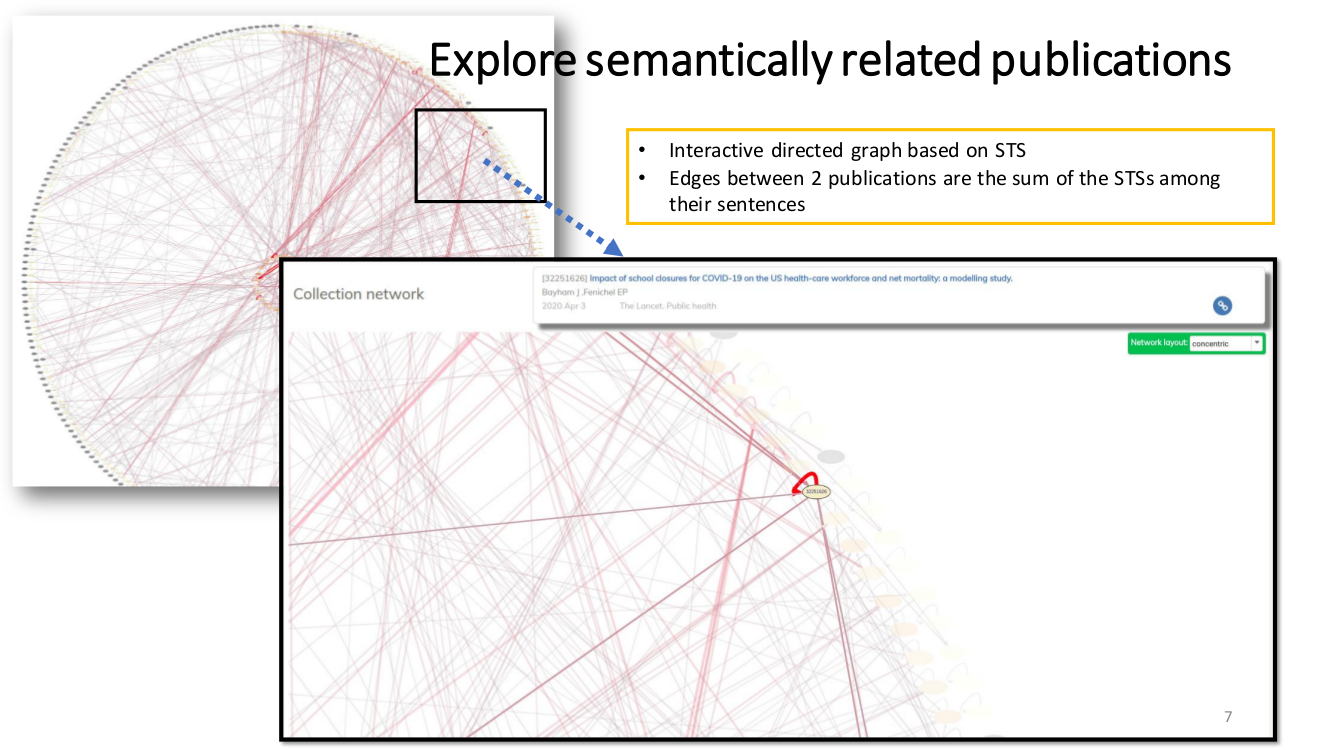
TRANSVERSAL READING. We propose a semantically-guided transversal reading. We believe that this type of reading can significantly benefit the process of grasping the prominent opinion and state-of-the-art of a particular aspect. Our strategy to provide this feature was to interlink all semantically related sentences
by semantic-textual-similarity (STS).
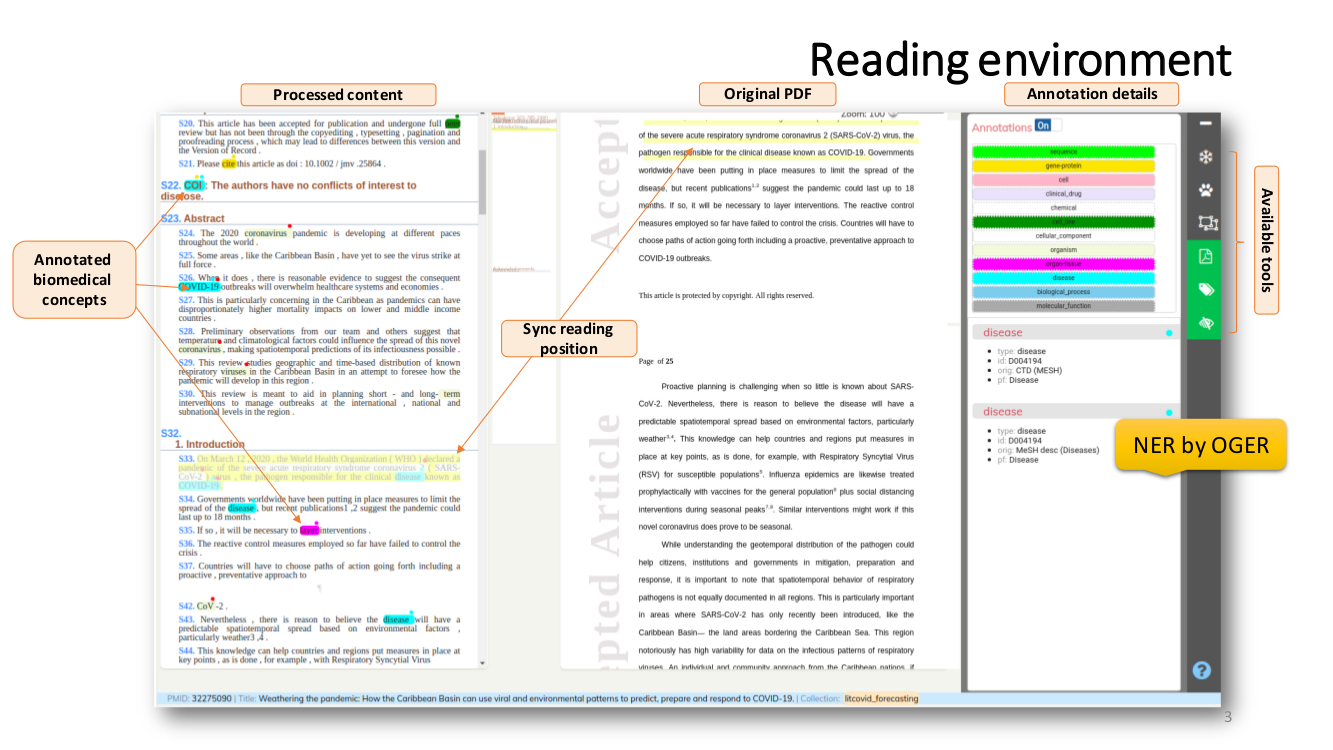
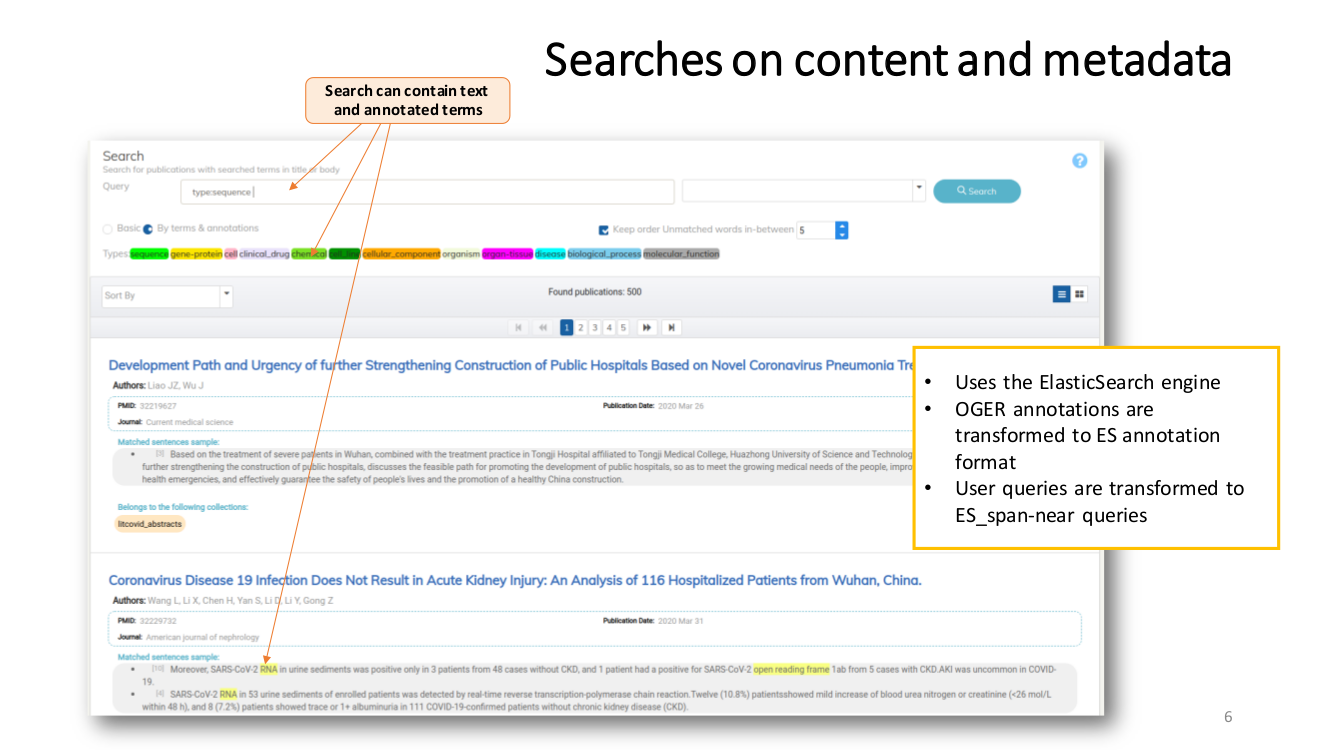
SEMANTIC ENRICHMENT. We enrich the literature with named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD), using the major life science databases as entity sources, enable named-entity searches, provide network-graphs of the most interconnected publications and, an interactive tool to highlight the most central statements within an article.

Methodology
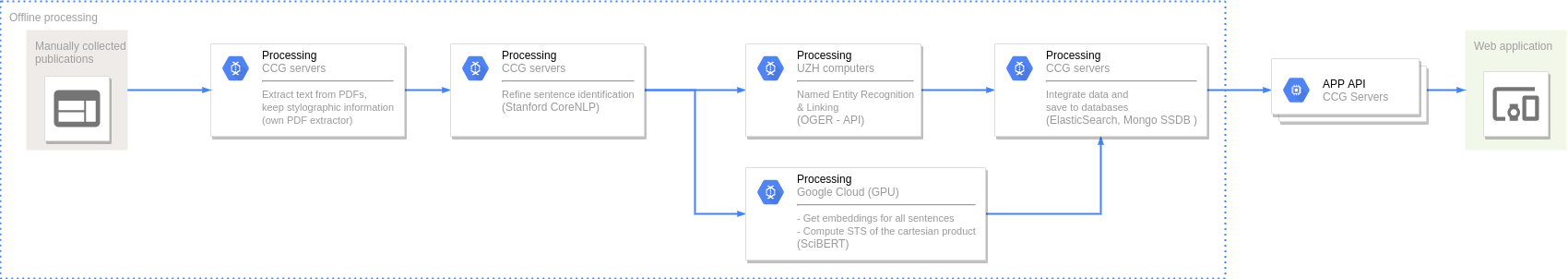
Named Entity Recognition and Disambiguation (NERD). These capabilities are provided by OGER, a state-of-the-art biomedical NER annotator which in turn depends on the Bio Term Hub (BTH). BTH is a combined terminological resource created by dynamically sourcing entity names and their identifiers from reference databases.
The OntoGene’s Biomedical Entity Recogniser (OGER) is a RESTful web service implemented on top of the BTH which allows a remote user to batch annotate a collection of documents.
Semantic Textual Similarity (STS). Our approach to measure STS is representing the sentences as embeddings and then use the cosine between two embeddings as their semantic similarity.
To compute the embeddings we used SciBERT, an unsupervised transformer language model pre-trained in the scientific literature. First, we map tokens to embeddings and then apply mean pooling to get fixed-sized sentence vectors.
Due to the lack of STS corpora specific to the COVID-19 literature we did not apply any fine-tuning.